Alzheimer's Disease Treatments with NADH
Summary: Good news, a FDA Approved clinical study proved that after 6 months of taking 10mg NADH daily, all (100%) of the Alzheimer’s disease patients showed no evidence of cognitive deterioration and had significantly higher scores on the Mattis Dementia Rating Scale (MDRS) tests, when compared to Alzheimer's disease patients taking a placebo (sugar pill).
10mg NADH daily, all (100%) of the Alzheimer’s disease patients showed no evidence of cognitive deterioration and had significantly higher scores on the Mattis Dementia Rating Scale (MDRS) tests, when compared to Alzheimer's disease patients taking a placebo (sugar pill).
Under the watchful eyes of one of the most prestigious research hospitals in the United States, Georgetown University Medical Center ran a FDA Approved clinical trial on the effects of NADH on Alzheimers patients. This randomized, placebo-controlled, matched pairs, double-blind, 6-month clinical study was initiated to test the effects of NADH on Alzheimer's disease patients. Twelve (12) pairs of subjects were matched for age and baseline scores on the Mattis Dementia Rating Scale (MDRS) and Mini Mental Stare Examination (MMSE). At the beginning of the clinical test, there were no baseline differences between the groups with respect to age, duration of the disease, months since diagnosis, or their performance on their tests. After 6 months of treatment, the patients treated with 10mg of NADH daily, showed no evidence of progressive cognitive deterioration and had significantly higher scores on the MDRS compared to the patients treated with the placebo. Further analysis of the MDRS subscales reveal significantly better performance by NADH patients in some areas.
The Doctors that ran the clinical trial study recently stated that using a higher daily dose of NADH would provide an even better result than the clinical trial result. The new recommendation is for an Alzheimer’s disease patient to take 40mg (or more) of NADH daily to experience the better than clinical trial result.
Clinical Study Publications (click on the link to download):
Alzheimer's Patients Taking NADH Showed No Evidence of Progressive Cognitive Deterioration
NADH Demonstrates Cognitive Impairment Improvements in Alzheimer's Patients
Successfully Treating Alzheimer's disease with NADH
Dr Birkmayer is making the presentation [01:47]
The Full Text of "Alzheimer's disease and NADH"
(This Full Text section may repeat video(s) & clinical study publications found in the Summary)
The Clinical Testing:
 Medical science has proved that Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease attack brain tissue in similar ways. Since the mid-1980's NADH has successfully been treating Parkinson's disease. NADH is a co-enzyme and plays key roles within brain cells including: ATP energy production and stimulates dopamine (a brain chemical) production. In other clinical trials, NADH has IMPROVED the cognitive functioning in Parkinson’s disease patients, patients suffering from depression have improved, and patients with Alzheimer's disease have shown documented improvements. The Alzheimer's disease patients were tested in "open trials" (where patients knew they were taking NADH) and not under the watchful eyes of a medical science controlled clinical trial.
Medical science has proved that Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease attack brain tissue in similar ways. Since the mid-1980's NADH has successfully been treating Parkinson's disease. NADH is a co-enzyme and plays key roles within brain cells including: ATP energy production and stimulates dopamine (a brain chemical) production. In other clinical trials, NADH has IMPROVED the cognitive functioning in Parkinson’s disease patients, patients suffering from depression have improved, and patients with Alzheimer's disease have shown documented improvements. The Alzheimer's disease patients were tested in "open trials" (where patients knew they were taking NADH) and not under the watchful eyes of a medical science controlled clinical trial.
To provide Alzheimer’s disease testing results validation showing NADH does provide significant positive effects, a FDA Approved clinical trial was started at the Georgetown University Medical Center. They managed the clinical trail. It was a randomized, placebo-controlled, matched pairs, double-blind, 6-month clinical study. To further describe the testing method: Twelve (12) pairs of subjects were matched for age and baseline scores on the Mattis Dementia Rating Scale (MDRS) and Mini Mental Stare Examination (MMSE). At the beginning of the clinical trial, there were NO BASELINE DIFFERENCES between the groups with respect to age, duration of the disease, months since diagnosis, or their performance on their tests. In a double blind study, neither the patients, nurses, administrators, nor the doctor administering the NADH know which pill is NADH, and which pill is the placebo (the sugar pill).
After 6 months of treatment, the patients treated with 10mg of NADH daily showed no evidence of progressive cognitive deterioration and had significantly higher scores on the MDRS compared to the patients treated with the placebo. Further analysis of the MDRS subscales reveal significantly better performance by the NADH patients on measures of verbal fluency, visual constructional ability and a trend for better performance on a measure of abstract verbal reasoning. There were no differences between the groups on measures of attention, memory or the clinician ratings of dementia severity (a Clinical Dementia Rating).
The clinical study (available in the link below) is highly technical in nature. It is difficult to read, and is usually read by a doctor or a healthcare professional. We recommend you take the study to a doctor or healthcare provider and discuss its results.
The clinical study teaches: "the younger patients, with a shorter duration of the disease, have a best chance to obtain the most significant improvements." This Alzheimer clinical trial proved that after 6 months of taking 10mg of NADH daily 100% of the Alzheimer’s disease patients showed no evidence of cognitive deterioration and had significantly higher scores on the MDRS compared to the patients treated with the placebo. If the Alzheimer’s disease is in the most advanced stages, it is very difficult to show improvement. The clinical study recommended 10mg of NADH daily. The Doctors who participated in the the study recommended an Alzheimer’s disease patient should take 40mg (or more) of NADH daily to experience the benefits similar to those received in the study.
NADH: A Background
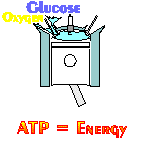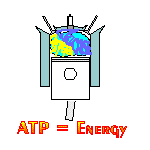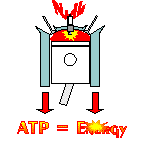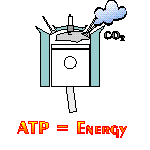 The NADH Alzheimer’s disease treatment comes from a co-enzyme called NADH or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide with the ‘H’ standing for hydrogen. What makes NADH promising to treat Alzheimers is Mother Nature uses NADH to create ATP energy in brain cells and it stimulates the production of necessary brain chemicals (also called neurotransmitters) for healthy brain functioning. The creation of ATP energy takes place in a process called "cellular respiration." Cellular respiration is not breathing. Cellular respiration is like a cellular engine. An engine used to power all living things (i.e., thought, memory, concentration, decision making, as well as muscle movements, heart beats, etc.). Just like a car engine, within the cellular respiration engine, all human cells bring in glucose (the fuel) and oxygen (the air) together, and with the spark of NADH (the spark plug) ATP is created to power all living things. Clinical testing has proven the more NADH a cell has, the more ATP the cell produces. Now a NADH nutritional supplement can of resupply cells with ATP energy. For more information about how Mother Nature uses NADH to create ATP, see this website's section called The Guided Tour.
The NADH Alzheimer’s disease treatment comes from a co-enzyme called NADH or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide with the ‘H’ standing for hydrogen. What makes NADH promising to treat Alzheimers is Mother Nature uses NADH to create ATP energy in brain cells and it stimulates the production of necessary brain chemicals (also called neurotransmitters) for healthy brain functioning. The creation of ATP energy takes place in a process called "cellular respiration." Cellular respiration is not breathing. Cellular respiration is like a cellular engine. An engine used to power all living things (i.e., thought, memory, concentration, decision making, as well as muscle movements, heart beats, etc.). Just like a car engine, within the cellular respiration engine, all human cells bring in glucose (the fuel) and oxygen (the air) together, and with the spark of NADH (the spark plug) ATP is created to power all living things. Clinical testing has proven the more NADH a cell has, the more ATP the cell produces. Now a NADH nutritional supplement can of resupply cells with ATP energy. For more information about how Mother Nature uses NADH to create ATP, see this website's section called The Guided Tour.
Doctors that have tested NADH on patients have stated:
- NADH is a safe, natural compound that has shown much promise with patients in Europe
- Much more extensive research and testing is needed
- The clinical trials for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease patients is a significant step, down a long road to investigate the many potential benefits of this natural co-enzyme called NADH.
NADH is a co-enzyme. The American Heritage Dictionary defines a co-enzyme as:
- a non-protein organic substance that usually contains a vitamin or mineral and combines with a specific protein, to form an active enzyme system
NADH is not a drug, not a stimulant, and is non-toxic even in very large dosages. NADH was tested for 26 weeks at 1,000mg daily and was found not to have any negative side effects. NADH is already found within every human cell. Because it is already in every human cell, NADH can safely be taken with any other medication. After extensive safety testing, it was proven NADH does not have any negative side effects and no adverse drug interactions. See this website’s section called Safety First for more information.
The most important things to remember about the NADH is some level of NADH is found within every human cell, and:
- NADH increases the levels of ATP cellular energy. The more NADH cells have, the more ATP energy cells produce. NADH increases cell longevity.
- NADH is a powerful antioxidant, and scavenger of free radicals. According to Dr. Passwater, "NADH may just be the most powerful antioxidant"
- NADH is the active ingredient in cellular DNA repair. NADH plays an active role in the repair of damaged cells.
- NADH stimulates the immune system
- NADH enhances the production of dopamine, a very important brain chemical (also known as a neurotransmitter)
- NADH increases the bio-availability of nitric oxide, known to provide increased blood flow, oxygen delivery, glucose uptake, muscle velocity, power output, and muscle growth
Alzheimer's disease: The ILLINESS
 Alzheimer's disease is a progressive disease that destroys memory and other important brain / mental functions. Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia. Dementia is a group of brain disorders resulting in the loss of intellectual and social skills. These changes interfere with day-to-day life. When Alzheimer's brain cells degenerate (or lose energy), they die. Dying brain cells caused a steady decline in memory and other brain / mental functions.
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive disease that destroys memory and other important brain / mental functions. Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia. Dementia is a group of brain disorders resulting in the loss of intellectual and social skills. These changes interfere with day-to-day life. When Alzheimer's brain cells degenerate (or lose energy), they die. Dying brain cells caused a steady decline in memory and other brain / mental functions.Current Alzheimer's disease medications may temporarily improve symptoms. This can sometimes help some people with Alzheimer's disease maintain their independence.
There is no known cure for Alzheimer's disease. At first, increasing forgetfulness, mild confusion, and difficulty organizing thoughts may be the only symptoms.
Over time, the disease robs more of a person’s memory. The rate at which symptoms worsen varies from person to person. Brain changes associated with Alzheimer's disease leads to growing trouble, such as:
- Memory, repeating statements or questions over and over, not realizing the question has already been asked before
- Forget conversations, appointments or events, and not remember them later
- Routinely misplace possessions, often putting them in illogical locations
- Eventually forget the names of family members and everyday objects
- Disorientation and misinterpreting spatial relationships
- People with Alzheimer's disease lose their sense of what day it is, what season it is, where they are or even their current life circumstances
- Alzheimers disrupts the brain's ability to interpret what is seen, making it difficult to understand the surroundings. Eventually, these problems may lead to getting lost even in familiar places.
- Over time, the ability to read and write declines.
- Thinking and reasoning declines
- Making good judgments and good decisions declines
- Responding effectively to everyday problems, such as food burning on the stove or unexpected driving situations, becomes increasingly challenging.
- Planning and performing familiar tasks becomes a problem
- Changes in personality and behavior can affect the way a person acts and how they feel.
Alzheimer’s disease symptoms include:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Mood swings
- Distrust in others
- Irritability and aggressiveness
- Changes in sleeping habits
- Wandering
- Loss of inhibitions
- Delusions, such as believing something has been stolen
Many important skills are not lost until very late in the disease. These important skills include the ability to read, dance and sing, enjoy old music, engage in crafts and hobbies, tell stories, and reminisce. This is because information, skills and habits learned early in life are among the last abilities to be lost as Alzheimer's disease progresses. Capitalizing on these abilities can allow a person to continue to have successes and maintain a quality of life even when they are into the moderate phase of the disease.

Alzheimer’s disease: Who Will Be Affected?
- Age. The risk of having Alzheimer's disease or dementia increases with age. Alzheimer’s is NOT part of normal aging process, but a person’s risk increases greatly after age 65. Nearly half of those older than age 85 have some form of Alzheimer's or dementia
- Heredity. People with rare genetic DNA are virtually guarantee they will develop Alzheimer's and begin experiencing symptoms in their early 30's. The risk of developing Alzheimer's appears to be somewhat higher if a first-degree relative — a parent or sibling — has the disease.
- Sex. Women may be more likely than are men to develop Alzheimer's disease, (In part because women live longer.)
- Past head trauma. People who've had a severe head trauma or repeated head trauma appear to have a greater risk of having Alzheimer's disease
-
Lifestyle and heart health: Evidence suggests that the same factors that put a person at risk for heart disease also increase the the risk that they will develop Alzheimer's. The evidence examples include:
- Lack of exercise
- Smoking
- High blood pressure
- High blood cholesterol
- Elevated homocysteine levels
- Poorly controlled diabetes
- A diet lacking in fruits and vegetables
- Studies have found an association between lifelong involvement in mentally and socially stimulating activities DOES REDUCE the risk of getting Alzheimer's disease.
Alzheimer’s disease: Diagnosis & Current Treatment:
 Although Alzheimer’s disease can't be cured, there are medications that are known to improve Alzheimer’s symptoms.
Although Alzheimer’s disease can't be cured, there are medications that are known to improve Alzheimer’s symptoms.
Current Alzheimer's medications can help (for a time) with memory symptoms and other cognitive changes.
Two types of drugs are currently used to treat cognitive symptoms:
Cholinesterase inhibitors. These drugs work by boosting the chemical levels used in cell-to-cell communications that have become depleted in the Alzheimer's disease brain. Most patients taking these drugs can expect to keep their current symptoms at bay for a time.
Less than half of those taking these drugs can expect to have any improvement. Commonly prescribed cholinesterase inhibitors include donepezil (Aricept), galantamine (Razadyne) and rivastigmine (Exelon). The main side effects of these drugs include diarrhea, nausea and sleep disturbances.
Memantine (Namenda). This drug works in another brain cell communication network and slows the progression of symptoms with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. It's sometimes used in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor.
What else can be done to avoid Alzheimer's disease? Follow a brain-protective diet. This includes lots of healthy omega-3 fats, fish, fruits, and vegetables that are high in antioxidants. Eat avocado, nuts, and flax seed. Stay away from refined sugar, which is inflammatory. Brain inflammation is linked to Alzheimer’s.
• Stay at your ideal body weight.
• Exercise daily. Take a brisk walk, swim, or perform any activity that will help get oxygen to the brain.
• Reduce stress. Meditation or tai chi can help.
• Perform mental challenging tasks. Do puzzles, learn a language, take music lessons, read challenging books.
• Provide emotional support. Help and support people others (for example help others with Alzheimer’s and their caregivers.)
Conclusion:
 With this knowledge, it stands to reason that a daily NADH nutritional supplement will help a Alzheimer's disease patient. Use only the stabilized form of NADH (See this website's section called Let the Buyer Beware) The clinical trial teaches: "the younger patients, with a shorter duration of the disease, have a best chance to obtain the most significant improvements." The Alzheimer clinical trial proved that after 6 months of taking 10mg of NADH daily 100% of the Alzheimer’s disease patients showed no evidence of cognitive deterioration and had significantly higher scores on the MDRS compared to the patients treated with the placebo. NADH is not a cure for Alzhiemers disease. If the Alzheimer’s disease is in the most advanced stages, it is very difficult to show improvement. The clinical trial recommended 10mg of NADH daily. The Doctors who ran the trail recently recommended an Alzheimer’s disease patient take 40mg (or more) of NADH daily to experience the benefits similar to those received in the study.
With this knowledge, it stands to reason that a daily NADH nutritional supplement will help a Alzheimer's disease patient. Use only the stabilized form of NADH (See this website's section called Let the Buyer Beware) The clinical trial teaches: "the younger patients, with a shorter duration of the disease, have a best chance to obtain the most significant improvements." The Alzheimer clinical trial proved that after 6 months of taking 10mg of NADH daily 100% of the Alzheimer’s disease patients showed no evidence of cognitive deterioration and had significantly higher scores on the MDRS compared to the patients treated with the placebo. NADH is not a cure for Alzhiemers disease. If the Alzheimer’s disease is in the most advanced stages, it is very difficult to show improvement. The clinical trial recommended 10mg of NADH daily. The Doctors who ran the trail recently recommended an Alzheimer’s disease patient take 40mg (or more) of NADH daily to experience the benefits similar to those received in the study.
NADH is already found within all human cells. The more NADH the cell has, the more ATP energy the cell produce. ATP energy enables the brain cells to provide: thinking, memory, concentration, decision making, mental clarity, etc. ATP enables muscles to provide: movement, stamina, physical endurance, etc. See this website’s section called ATP Energy for more information. NADH stimulates the immune system used to fight diseases, and most importantly NADH enhances the production of the brain chemical called dopamine. Clinical testing proves sufficient levels of dopamine are required for normal brain functions.
NADH is safe to take, has no drug interactions, nor any adverse side effects so a person may continue to take their medications when taking a NADH nutritional supplement.
 The creators of NADH in a stabilized form have decades of success treating patients with chronic and degenerative diseases in Europe. To validate a belief that NADH will help Alzheimers patients a clinical study was started. The clinical study results state patients taking 10mg of NADH daily showed no evidence of progressive cognitive deterioration and had significantly higher scores on the Mattis Dementia Rating Scale (MDRS) and Mini Mental Stare Examination (MMSE) when compared to the patients treated with the placebo (a sugar pill).
The creators of NADH in a stabilized form have decades of success treating patients with chronic and degenerative diseases in Europe. To validate a belief that NADH will help Alzheimers patients a clinical study was started. The clinical study results state patients taking 10mg of NADH daily showed no evidence of progressive cognitive deterioration and had significantly higher scores on the Mattis Dementia Rating Scale (MDRS) and Mini Mental Stare Examination (MMSE) when compared to the patients treated with the placebo (a sugar pill).
The brain and the muscles need high levels of NADH. If the cell's NADH levels are depleted, the brain will no longer function properly. It is NOT known how NADH becomes depleted from the body. Today, a scientific breakthrough has enabled NADH to be manufactured in a stabilized form. A person can restore their NADH levels by taking a NADH nutritional supplement. The same NADH nutritional supplement used in the Alzheimer’s clinical study is available from this website or other high quality nutritional supplement stores. Use only the stabilized form of NADH (See this website's section called Let the Buyer Beware) A high quality FDA licensed laboratory environment is used to manufacture NADH which ensures that each and every tablet or lozenge is of the highest, professional grade standard.
.
Take a copy of the clinical study to the patient's doctor or healthcare professional and discuss the options. The clinical study is yours to take. Order NADH today. You will be glad you did!

Read Publications / Clinical Studies (click on the link to download):
Alzheimer's Patients Taking NADH Showed No Evidence of Progressive Cognitive Deterioration
NADH Demonstrates Cognitive Impairment Improvements in Alzheimer's Patients
NADH Clinically Demonstrates Benefits For Alzheimer's Patients
The More NADH in the Blood - the More ATP Energy is in the Cell
ENADA CoE1 NADH Nutritional Supplementation Elevates ATP Energy Within the Cell

Successfully Treating Alzheimer's disease with NADH
Dr Birkmayer is making the presentation [01:47]

