Stand Up To Cancer with NADH Treatments
 Summary: Good news, in
Summary: Good news, in  clinical tests cancer cell growth was inhibited (or slowed) by 92% in the presence of NADH. In other words, cancer cells grew at 100% WITHOUT NADH -- compared to a cancer cell growth of 8% WITH NADH present. When cancer cell growth is inhibited (or slowed) the human body's defense mechanisms fight off the cancer cells instead of being out numbered and over run with cancer cells. Cancer cells grow at an incredibly fast rate daily. NADH clinical tests were performed on different kinds of cancer, including the malignant tissues of colon carcinoma, laryngeal carcinoma, breast carcinoma, cervix carcinoma as well as against murine fibrosarcoma (See study results in the link below).
clinical tests cancer cell growth was inhibited (or slowed) by 92% in the presence of NADH. In other words, cancer cells grew at 100% WITHOUT NADH -- compared to a cancer cell growth of 8% WITH NADH present. When cancer cell growth is inhibited (or slowed) the human body's defense mechanisms fight off the cancer cells instead of being out numbered and over run with cancer cells. Cancer cells grow at an incredibly fast rate daily. NADH clinical tests were performed on different kinds of cancer, including the malignant tissues of colon carcinoma, laryngeal carcinoma, breast carcinoma, cervix carcinoma as well as against murine fibrosarcoma (See study results in the link below).The Doctors who ran the clinical studies recommend a cancer patient take 40mg to 80mg of NADH daily to stop the progression of cancerous cells. It was recommended to take as much as 160mg daily of NADH if the cancer patient already has a cancerous tumor. (See the video below called Cancer Growth Slowed with NADH)
Clinical Studies & Publications (click on the link to download):
Cancer Growth / Tumor Growth Slowed when NADH was Applied - a Clinical Study
Chemistry, Biology and Cancer: The primary cause of (all types of) cancer is the replacement of oxygen in cells during normal cellular respiration. Oxygen is replaced with the fermentation of sugar during "cancer (cell) respiration". In (cancer) fermentation three units of ATP are produced, whereas in normal cellular respiration 36 units of ATP are produced. Cancer cells (all types) will not / cannot reproduce in an ATP rich environment.
NADH inhibits Cancer Growth
NADH Inhibits the Growth of Tumors
(NADH Rapid Energy 20mg = MOJO 20mg = 20mg ENADA)
Cancer Growth Inhibited (slowed) with NADH
Dr Birkmayer is making the presentation [06:22]
The Full Text of "Stand Up To Cancer with NADH"
(This Full Text section may repeat video(s) & clinical study publications found in the Summary)
The Clinical Testing: Some Chemistry and Biology of Cancer
Dr. Warburg won a Noble Prize for his work on "the metabolism of cancer tumors and the cellular respiration of cancer cells." In simple terms, Dr. Warburg states, "The primary cause of (all types of) cancer is the replacement of oxygen during the normal cellular respiration process. Oxygen is replaced with the fermentation of sugar during cancer (cell) respiration. In cancer (cell) fermentation, three units of ATP are produced, whereas in normal, healthy cellular respiration 36 units of ATP are produced. Cancer cells will not and cannot reproduce in ATP rich environments." The more NADH a cell has – the more ATP the cell produces. (See the clinical study in link below.)
A deficiency of ATP is indeed a cause of many different types of cancers (not all cancers). Supplying ATP from a dietary supplement outside the cell might be a reasonable cancer treatment approach. The ATP would inhibit the unlimited mass multiplication of cancer tumor cells. But an ATP nutritional supplement is not available. Science has not been able to create a stabilized ATP nutritional supplement, but ADH creates ATP.
Question: How can a cancer patient compensate for a cellular ATP deficiency within their cancer cells? Clinical studies have shown cellular ATP levels can be increased. The studies show the more NADH a cell has, the more ATP the cell produces. (See the link below) NADH is available in a daily nutritional supplement. If normal healthy cells are under attack from cancer, the immune system can fight off and beat the cancer cell growth. The immune system would need fighting reinforcements (ATP) being supplied by NADH. The healthy immune system may stand up to cancer and beat it. Depending on the length of the time from first diagnosis, the amount of the cancer cells present, and a few other factors, an abundant amount of ATP may be able to turn the tide of battle and win the fight against cancer cell growth.
When cellular respiration and cell division is normalized (and made healthy), the growth of cancer cells are stopped. There are three NADH functions that are used in fighting off cancer's massive growth, and inhibiting the tumor cell formation:
- NADH is an essential factor for cellular DNA repair
- NADH is the strongest biological antioxidant and a scavenger of free radicals.
- NADH increases ATP within the cell
NADH: A Background
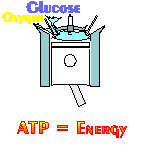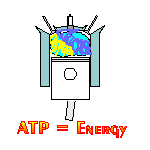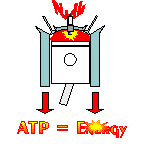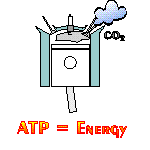 A NADH cancer cell and/or tumor cell treatment comes from a co-enzyme called NADH or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide with the ‘H’ standing for hydrogen. What makes NADH promising is Mother-Nature uses NADH to create ATP (cellular energy) within all human cells. ATP creation takes place in a process called "cellular respiration." Cellular respiration is not breathing. Cellular respiration is like a car engine where fuel and air mix to create power. NADH creates ATP in a cellular engine. It is the engine that powers all living things (i.e., thought, memory recall, concentration, muscle movement, heart beats, the immune system, etc.). Within the cellular respiration engine, all human cells bring glucose (fuel) and oxygen (air) together, and with the spark of NADH (the spark plug) creates ATP (the power). Cancer cell growth is inhibited in ATP rich cellular environments. Science has not been able to create an ATP nutritional supplement. Science has not be able to stabilize ATP. But clinical studies have proved adding more NADH to the cell, increases the amount of ATP within the cell.
A NADH cancer cell and/or tumor cell treatment comes from a co-enzyme called NADH or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide with the ‘H’ standing for hydrogen. What makes NADH promising is Mother-Nature uses NADH to create ATP (cellular energy) within all human cells. ATP creation takes place in a process called "cellular respiration." Cellular respiration is not breathing. Cellular respiration is like a car engine where fuel and air mix to create power. NADH creates ATP in a cellular engine. It is the engine that powers all living things (i.e., thought, memory recall, concentration, muscle movement, heart beats, the immune system, etc.). Within the cellular respiration engine, all human cells bring glucose (fuel) and oxygen (air) together, and with the spark of NADH (the spark plug) creates ATP (the power). Cancer cell growth is inhibited in ATP rich cellular environments. Science has not been able to create an ATP nutritional supplement. Science has not be able to stabilize ATP. But clinical studies have proved adding more NADH to the cell, increases the amount of ATP within the cell.
There are many NADH supplements available on the market (over 30 of them). Use ONLY the NADH co-enzyme products created in a stabilize form. You can find the stabilized form of NADH from this website and in high quality nutritional supplement stores. For more information see this section's website called Let the Buyer Beware. For more information about Mother Nature's production of ATP by NADH see this website’s section called The Guided Tour.
The Doctors that have tested NADH on patients have stated:
- NADH is a safe, natural compound that has shown much promise with patients in Europe
- Much more extensive research and testing is needed
- The clinical testing for the treatment of the cancer cells and tumor cells are significant steps, down a long road to investigate the many potential benefits of this natural co-enzyme called NADH.
NADH is a co-enzyme. The American Heritage Dictionary defines a co-enzyme as:
- a non-protein organic substance that usually contains a vitamin or mineral and combines with a specific protein, to form an active enzyme system
NADH is not a drug, not a stimulant (like caffeine) and non-toxic even in large dosages. NADH was tested for 26 weeks at 1,000mg daily and no negative side effects where observed. Because NADH is already found within every human cell, NADH can safely be taken with any other medication or medical treatment. After extensive safety testing, it was proven NADH does not have any negative side effects and no adverse drug interactions. See this website’s section called Safety First for more information.
The most important things to remember about the NADH, which is already found within every human cell are:
- NADH increases the levels of ATP which increases the level of energy. The more NADH cells have -- the more ATP cells produce. NADH increases cell longevity.
- NADH is a powerful antioxidant, a scavenger of free radicals. According to Dr. Passwater, "NADH may just be the most powerful antioxidant"
- NADH is the active ingredient in cellular DNA repair. NADH plays an active role is repairing cell damage
- NADH stimulates the immune system
- NADH enhances the production of dopamine, a very important brain chemical (also known as a neurotransmitter)
- NADH increases the bio-availability of nitric oxide, known to provide increased blood flow, oxygen delivery, glucose uptake, muscle velocity, power output, and muscle growth
Cancer and Tumors: The illness
Cancer refers to any one of a large number of diseases characterized by the development of abnormal cells that divide uncontrollably and have the ability to infiltrate and destroy normal body tissue. Cancer cells have the ability to spread throughout the body quickly.
Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the United States. Survival rates are improving for many types of cancer, thanks to improvements in early cancer screening and new cancer treatments
- Lump or area of thickening that can be felt under the skin
- Fatigue
- Weight changes, including unintended weight loss or weight gain
- Skin changes, such as yellowing, darkening or redness of the skin, including sores that won't heal, or changes to existing moles in shape and color
- Changes in bowel or bladder habits
- Persistent cough
- Difficulty swallowing
- Hoarseness
- Persistent indigestion or discomfort after eating
- Persistent, unexplained muscle or joint pain
- Persistent, unexplained fevers or night sweats
Cancer is caused by changes (or mutations) to the healthy cell's DNA. The DNA inside a cell contains the set of instructions telling the cell how to grow and how to divide. Errors in these instructions may cause a cell to become cancerous.
What do gene mutations (DNA mutations) do? A gene mutation can instruct a healthy cell to:
- Allow for rapid growth. A gene mutation can tell a cell to grow and divide more rapidly. This creates many new cells that all have that same mutation.
- Fail to stop growing, or an uncontrolled cell growth. Normal cells know when to stop growing, so that a person has just the right number of each type of cell. A mutation in a tumor suppressor gene (its DNA) allows cancer cells to continue growing and growing and accumulating.
- Make a mistake when repairing a cell's DNA. Cell DNA repair genes look for errors in a cell's DNA and makes corrections. A mutation (a mistake) in a DNA repair gene may mean that other errors aren't corrected. This action leads cells to become cancerous.
What can cause gene mutations? Truth is gene mutations can occur for several reasons, for example:
- There are gene mutations a person (a cancer patient) is born with. A person may be born with a genetic mutation that was inherited from their parents. This type of mutation account for a small percentage of cancers.
- Gene mutations that occur after birth. Most gene mutations occur after the person is born.
- There are many environmental forces that can cause gene mutations, e.g., smoking, radiation, cancer-causing pollutants, asbestos, carcinogens, obesity (yes obesity), hormones, chronic inflammation, lack of exercise (yes the lack of exercise), viruses and much, much more.
Methods of cancer and tumor detection vary and include visual observation, palpation, X-ray study, endoscopy, CAT scans, ultrasound, or surgical biopsy. Tumors caught early (before they metastasis) have the best chances for a cure. Cancer is traditionally treated by surgery, chemotherapy, and/or radiation. Today there are a lot more treatments with fewer side effects, such as hormonal products, vaccines, cryosurgery (- freezing the tumor), gene therapy, and much more. These therapies have been developed to fight specific types of cancers. Many other treatments are still under research. The branch of medicine concerned with diagnosis, treatment, and research into the causes of cancer is called "oncology."
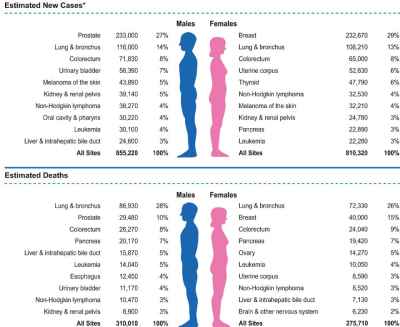
Cancer and Tumors: Who Will Be Affected?
While doctors have an idea of what may increase your risk of cancer, the majority of cancers occur in people who don't have any known risk factors. Factors known to increase a person's cancer risk include:
- Age: Cancer can take decades to develop. That is why most people diagnosed with cancer are 65 or older. While it's more common in older adults, cancer isn't exclusively an adult disease — cancer can be diagnosed at any age (even babies).
- Habits: Certain lifestyle choices are known to increase a risk of cancer. Smoking, drinking more than one drink a day (for women of all ages and everyone older than age 65) or two drinks a day (for men age 65 and younger), excessive exposure to the sun or frequent blistering sunburns, being obese, having unsafe sex can contribute to cancer. Changing these habits will lower the risk of cancer
- Family History: Only a small portion of cancers are due to an inherited condition. Also keep in mind that having an inherited genetic mutation doesn't necessarily mean the person will get cancer.
- Health Conditions: Some chronic health conditions, such as ulcerative colitis, can increase a person's risk of developing certain cancers.
- Environmental: The environment a person lives-in may contain harmful chemicals that can increase the risk of getting cancer. Example: Even if a person doesn't smoke, they might inhale secondhand smoke if they go where people are smoking or they live with someone who smokes. Chemicals in the home or in the workplace, such as asbestos and benzene, are associated with an increased risk of cancer.
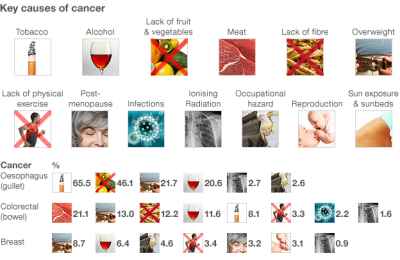
Cancer and Tumors: Current Types of Diagnosis and Current Treatment:
Diagnosing cancer at its earliest stages often provides the best chance for a cure. For a few cancers, studies show screening tests can save lives by diagnosing cancer early. For others, screening tests are recommended only for people with the highest risk.
Cancer Diagnosis:
- Physical Exam: The person or doctor may feel areas of the body for lumps that may indicate a tumor. During a physical exam, look for abnormalities, such as changes in skin color or enlargement of an organ. These symptoms may indicate the presence of cancer.
- Laboratory Tests: Laboratory tests, such as urine, blood, PSA, PAP tests, may help a doctor identify abnormalities that can be caused by cancer (e.g., leukemia)
- Imaging Tests: Imaging tests allow a doctor to examine a person's bones and internal organs in a noninvasive way. Imaging tests include a computerized tomography (CT) scan, bone scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound and X-ray, among others.
- Biopsy: During a biopsy, a doctor collects a sample of cells for laboratory testing. In many cases, a biopsy is the only way to definitively diagnose cancer. In the laboratory, a doctor looks at cell samples under a microscope. Normal cells look uniform. Normal cells have similar sizes and an orderly organization. Cancer cells look less orderly, with varying sizes and without apparent organization.
Cancer stages are generally indicated by Roman numerals — I through IV (1 through 4). The higher number indicates the more advanced cancer stage.
There are many cancer treatments available. Treatment options depend on several factors, such as the type and stage of the cancer, general health and a person's preferences. There are benefits and risks of each cancer treatment.
Cancer Treatments Objectives:
- Cure: The goal of treatment is to achieve a cure for cancer, allowing a person to live a normal life span.
- Primary Treatment: The goal of a primary treatment is to completely remove the cancer from the patient’s body or kill the cancer cells. Most time this treatment is accomplished with surgery. If the cancer is sensitive to radiation therapy or chemotherapy, that may be the primary treatment.
- Adjuvant Treatment: The goal of adjuvant therapy is to kill any cancer cells that may remain after the primary treatment. Adjuvant treatment is to reduce the chance that the cancer will recur. The most common adjuvant therapies include chemotherapy, radiation therapy and hormone therapy.
- Palliative Treatment: Palliative treatments help relieve the side effects caused by the cancer itself. Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy and hormone therapy can all be used. Medications may relieve symptoms of pain and shortness of breath.
Cancer Treatments:
- Surgery: The goal of surgery is to remove the cancer cells or as much of the cancer cells as possible.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-powered, highly focused energy beam (such as X-rays) to kill cancer cells.
- Stem Cell Transplant: Stem cell transplant is also known as a bone marrow transplant.
- Biological Therapy: Biological therapy uses your body's immune system to fight cancer. Biological therapy can help a patient’s immune system "see the cancer and attack it".
- Hormone Therapy: Some types of cancer are fueled by the patient’s body's hormones. Examples include breast cancer and prostate cancer. Removing those hormones from the body or blocking their effects -- It may cause the cancer cells to stop growing.
- Targeted Drug Therapy: Targeted drug treatment focuses on specific abnormalities within cancer that allow the cancer cells to survive.
- Clinical Trials: Clinical trials are studies to investigate new ways of treating cancer cells. Thousands of cancer clinical trials are underway. This website explains some successful clinical trials using NADH to inhibit (slow) the growth of cancer cells and tumor cells.
Conclusion:
It stands to reason that NADH might be able to help some people Stand Up To and Fight off some types of cancers. The good news is NADH is already found within all human cells. Mother Nature (the human body) already uses NADH to fight off cancer. NADH has no negative drug interactions, nor any adverse side effects. During the time of the clinical study, the clinical trial Doctors recommended 10mg to 20mg of NADH daily as a cancer treatment. Recently doctors have increased their recommended dosage to 40mg to 80mg of NADH daily to stop the progression of cancerous cells and tumor cells. In the video it is recommended as much as 160mg daily of NADH if the cancer patient already has a tumor. (See the video below called Cancer Growth Slowed with NADH)
The most important factors learned during the cancer clinical testing was: With 10mg to 20mg of NADH daily, in 92% of the cases NADH inhibited (slowed) the growth of cancer cells, and tumor cells. This was accomplished because:
- NADH is the strongest biological antioxidant, and a scavenger of free radicals
- An increase in a cell's NADH will increase the amount a cell's ATP. The noble prize winner Dr. Warburg says, "Cancer cells will not and cannot reproduce in ATP rich environments"
- NADH is an essential factor in cellular DNA repair
- NADH stimulates the immune system to fight off cancer cells and tumor cells
 Healthy cells need to contain high levels of NADH. When cellular NADH levels are depleted, cancer cells can rapidly multiply. It is NOT known how NADH becomes depleted from the body. Today, a scientific breakthrough has enabled NADH to be manufactured in a stabilized form. A person can restore their NADH cellular levels by taking a nutritional supplement. High NADH levels, mean high levels of cellular ATP. Use ONLY the stabilized form of NADH (See this website's section called Let the Buyer Beware) The same NADH used in the cancer and tumor cell clinical studies is available from this website or other high quality nutritional supplement stores.
Healthy cells need to contain high levels of NADH. When cellular NADH levels are depleted, cancer cells can rapidly multiply. It is NOT known how NADH becomes depleted from the body. Today, a scientific breakthrough has enabled NADH to be manufactured in a stabilized form. A person can restore their NADH cellular levels by taking a nutritional supplement. High NADH levels, mean high levels of cellular ATP. Use ONLY the stabilized form of NADH (See this website's section called Let the Buyer Beware) The same NADH used in the cancer and tumor cell clinical studies is available from this website or other high quality nutritional supplement stores.
With this knowledge it stands to reason, taking an NADH daily supplement could help some cancer patients. The clinical study prove having sufficient levels of NADH means having sufficient levels of ATP. (For more information about ATP, see this website's section called ATP Energy) Using NADH as a cancer therapy translates into a 92% reduction in the growth of some types of new cancer cells. In other words, NADH slows the majority of cancer cell growth. Depending on the patient’s cancer stage, type of cancer, length of time since the first diagnosis and other factors -- it may mean it does not help everyone. But helping some of the cancer sufferers, even a little is better than no help at all. The cancer patients can take NADH with any of their other cancer treatment medications.
Take a copy of the clinical study to your doctor or healthcare professional and discuss the options. The clinical study is available to take. Order the same NADH used in the clinical study from this website or other high quality nutritional supplement stores. A high quality FDA licensed laboratory environment used to manufacture the NADH we sell. It ensures that each and every tablet or lozenge is of the highest, professional grade standard.

Read the Publications and Clinical Studies (click link to download):
Cancer Growth / Tumor Growth Slowed when NADH was Applied - a Clinical Study
Chemistry, Biology and Cancer: The primary cause of (all types of) cancer is the replacement of oxygen in cells during normal cellular respiration. Oxygen is replaced with the fermentation of sugar during "cancer (cell) respiration". In (cancer cell) fermentation three units of ATP are produced, whereas in normal cellular respiration 36 units of ATP are produced. Cancer cells (all types) will not / cannot reproduce in an ATP rich environment.
NADH an all natural substance used successfully in Fighting Cancer
NADH for use in Prostate Cancer
NADH causes Cancer Cells to Stop Growing and Will Dissolve the Cancerous Tissue Cells
NADH known to Halt the Progression of Breast Cancer Cells
NADH Supplies Cellular ATP. Cancer Cells Can Not Grow in an ATP Rich Environment
NADH Inhibits Cancer Growth
NADH Inhibits the Growth of Tumors
NADH Inhibits the Growth of Tumors in Colorectal Cancer
NADH is Most Active in Fighting Cancer, AIDS and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Taking NADH and Co-enzyme Q10 once a day will maintain constant cellular levels of antioxidants (that fight off Cancer)
NADH used to Assist in Chemo Therapy because NADH plays a key role in DNA Repair & Cell Damage Repair)
NADH named a Medicine Chemistry's Anti-Cancer Agent (by the Chinese)
NADH Reduces the Incidence of Age-Related Diseases, such as Cancer, Diabetes, Immune Deficiencies and Cardiovascular Disorders
NADH used in Anti-Aging Therapeutics (NADH increases the lifespan of a cell)
The more NADH a cell has – the more ATP Energy cell produces
 Video Review
Video Review
(NADH Rapid Energy 20mg = MOJO 20mg = 20mg ENADA)
Cancer Growth Slowed with NADH -
Dr Birkmayer is making the presentation [06:22]



 Video Review
Video Review